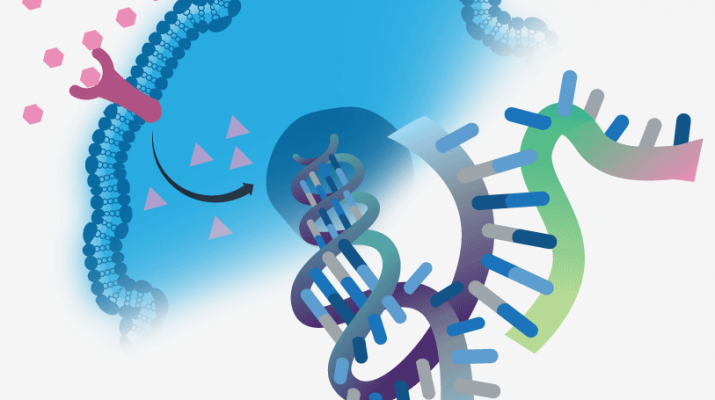
Gene expression is the process that leads to the synthesis of proteins in living cells. This complex process can be divided into three steps: transcription, translation, and post-translational modifications.
This article will discuss Power of Particles each step in detail and provide examples of how gene expression can be used in medical research and diagnostics.
What is Gene Expression?
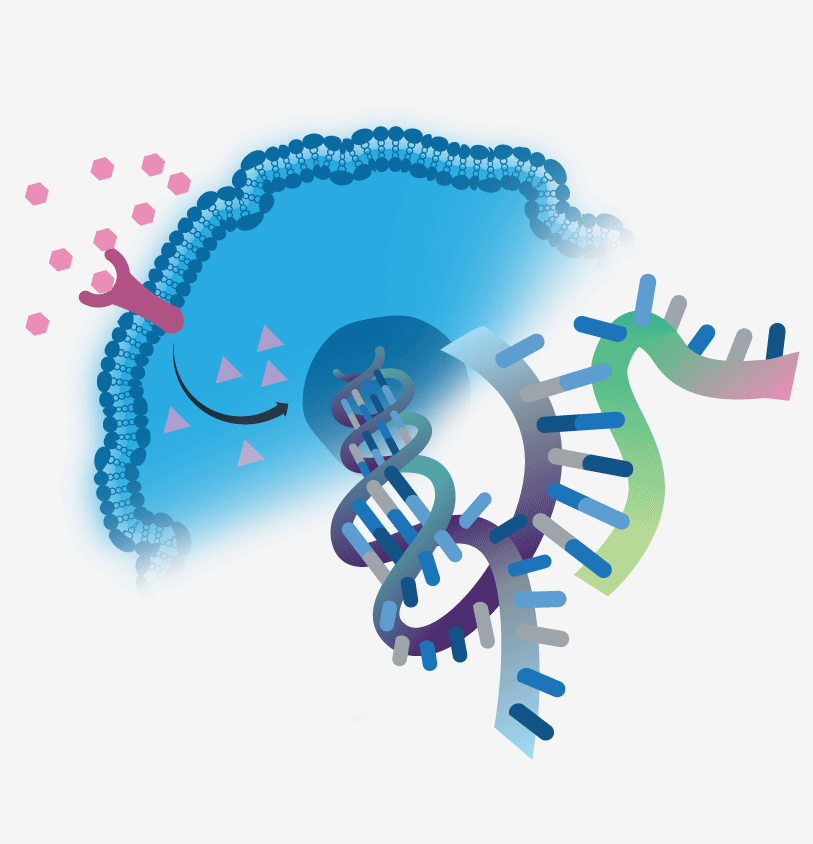
Gene expression is the process by which a gene’s instructions are converted into a protein. The gene is first copied into RNA (ribonucleic acid), and then the RNA molecule is used to make the protein. Gene expression can be controlled by environmental factors, such as hormones, or other genes can regulate it.
RNA is the molecule that helps carry the gene’s instructions from the cell’s nucleus to the ribosomes. The ribosomes are where proteins are made. The RNA molecule can be single-stranded or double-stranded.
There are three types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA is the type that carries the gene’s instructions from the nucleus to the ribosomes. tRNA helps bring amino acids to the ribosome, where they are joined together to make a protein. rRNA is a type of RNA that is found in ribosomes.
Three Processes of Gene Expression
There are three processes: transcription, translation, and post-transcriptional modification.
1) Transcription
It is the medical process of copying a gene’s instructions from DNA to RNA. The first step is called initiation. In this step, an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to the DNA.
The RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA and separates the two strands of DNA. The RNA polymerase then moves along the template strand of DNA and starts to make a complementary RNA strand.
2) Translation
It is the process of turning RNA into protein. A ribosome reads the mRNA molecule and assembles a protein molecule. The mRNA strand acts as a template, and the ribosomes add amino acids to it one at a time.
The sequence of codons on the mRNA strand determines the order of the amino acids in the protein. A codon is a three-letter unit on the mRNA strand that codes for an amino acid. There are 64 possible codons, but some code for the same amino acid.
The genetic code is the sequence of codons in DNA that determines the order of amino acids in a protein. The genetic code is the same for all living organisms.
3) Post-transcriptional Modification
It is the process of modifying RNA after transcribed from DNA. There are several post-transcriptional modifications, including splicing, editing, and capping.
Splicing is the process of removing introns and leaving only the exons. Introns are regions of DNA that do not code for proteins. Exons are the coding regions of DNA.
After the splicing process, the exons are joined together. It is called RNA editing.
Which Areas of Medical Sciences Gene Expression is Used?
Gene expression has, so far, been used in cancer treatment, neurology, immunology, and cardiology. It is also used in drug discovery and development.
Conclusion
Gene expressions are the key to many critical biological processes. By understanding how they work, you can unlock new and better ways to treat diseases, improve crops, and even create new life forms.